Annotations in Java
Annotations in Java :
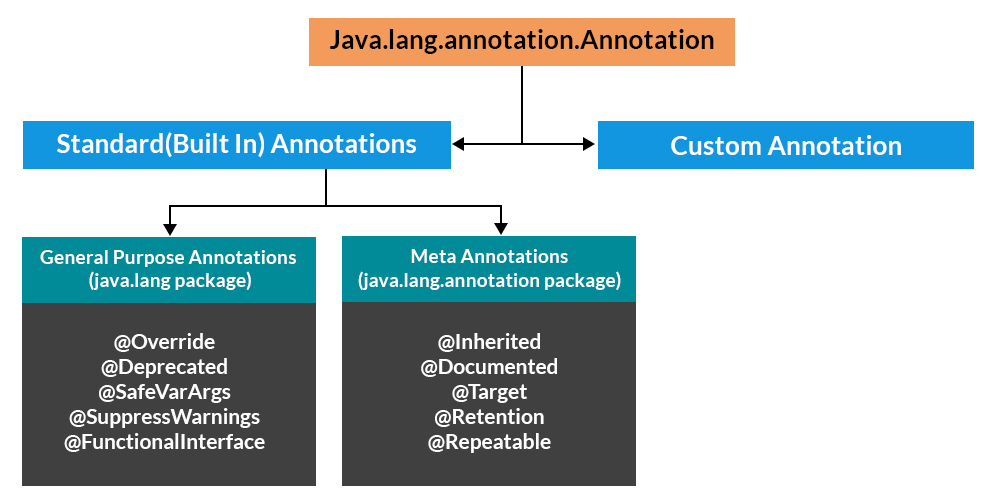
Annotations are used to provide additional information about a program.
- Annotations start with @
- Annotations do not change the action of a compiled program.
- Annotations help to associate metadata (information) to the program elements i.e. instance variables, constructors, methods, classes, etc.
- Annotations are not pure comments as they can change the way a program is treated by the compiler.
- Annotations basically are used to provide additional information, so could be an alternative to XML and Java marker interfaces.
Example 1 :
package java;
public class ann {
public void display(){
System.out.println("hell0 children");
}
}
class ch1 extends ann{
@Override
public void display() {
super.display();
// System.out.println("hello");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ch1 c1 = new ch1();
c1.display();
@SuppressWarnings({"deprecated","unused"})
int x;
}
}
Example 2 :
package javainheritance;
public class ann2 {
public void display(){
System.out.println("hell0 children");
}
}
class ch extends ann2 {
@Override
public void display() {
super.display();
// System.out.println("hello");
}
void cal(){
System.out.println("calculate");
}
public @interface myann{
int age() default 18;
String name();
}
@myann(
name = "akshay",age = 22
)
public static void main(String[] args) {
ch n = new ch();
n.display();
@SuppressWarnings({"deprecated","unused"})
int x;
n.cal();
System.out.println();
}
}
Comments
Post a Comment